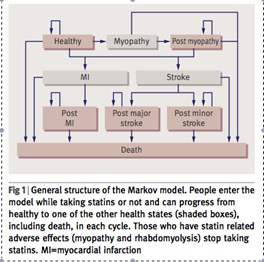
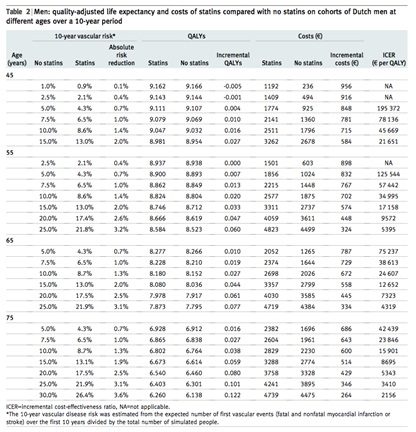
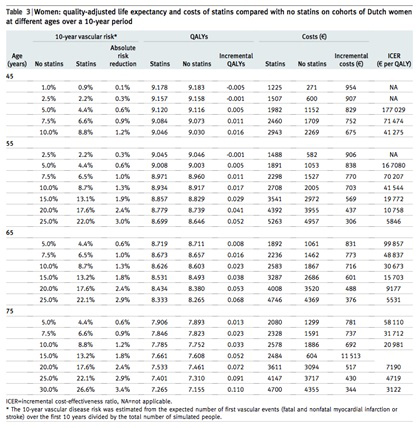
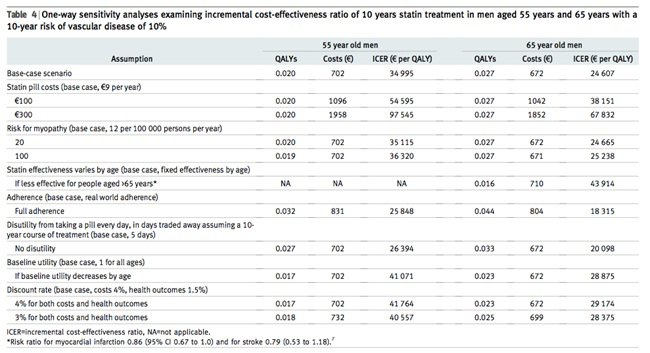
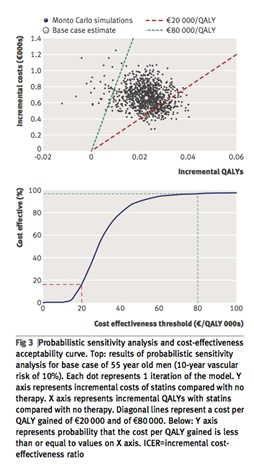
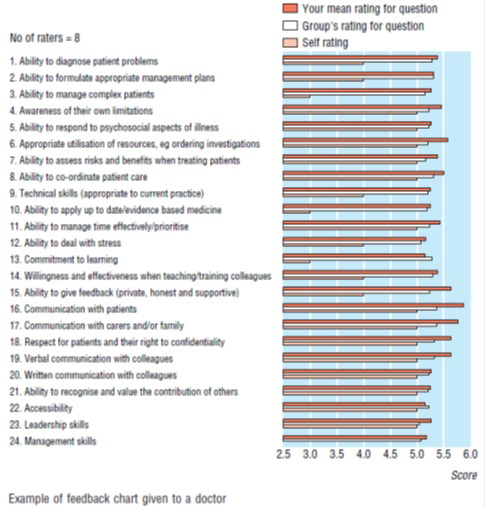
【文献名】
著者名:JC. Crosson, PA. Ohman-Strickland, D J. Cohen, EC. Clark, and BF. Crabtree.
文献タイトル:Typical Electronic Health Record Use in Primary Care Practices and the Quality of Diabetes Care.
雑誌名・書籍名:Ann Fam Med
発行年:May/June 2012 10:221-227.
【背景】
We implemented Secom’s EHR system into our 6 clinics these 4 years. But we could not always make use of its potential function as central portal system of medical information to improve our quality of care in daily practice. So, I am interested in this type of research to change our usage style of EHR. How can we find better use of EHR?
【要約】
<PURPOSE>
Recent efforts to encourage meaningful use of electronic health records (EHRs) assume that widespread adoption will improve the quality of ambulatory care, especially for complex clinical conditions such as diabetes. Cross-sectional studies of typical uses of commercially available ambulatory EHRs provide conflicting evidence for an association between EHR use and improved care, and effects of longer-term EHR use in community-based primary care settings on the quality of care are not well understood.
<METHODS >
We analyzed data from 16 EHR-using and 26 non-EHR-using practices in 2 northeastern states participating in a group-randomized quality improvement trial. Measures of care were assessed for 798 patients with diabetes. We used hierarchical linear models to examine the relationship between EHR use and adherence to evidence-based diabetes care guidelines, and hierarchical logistic models to compare rates of improvement over 3 years.
<RESULTS>
EHR use was not associated with better adherence to care guidelines or a more rapid improvement in adherence. In fact, patients in practices that did not use an EHR were more likely than those in practices that used an EHR to meet all of 3 intermediate outcomes targets for hemoglobin A1c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and blood pressure at the 2-year follow-up (odds ratio = 1.67; 95% CI, 1.12-2.51). Although the quality of care improved across all practices, rates of improvement did not differ between the 2 groups.
<CONCLUSIONS>
Consistent use of an EHR over 3 years does not ensure successful use for improving the quality of diabetes care. Ongoing efforts to encourage adoption and meaningful use of EHRs in primary care should focus on ensuring that use succeeds in improving care. These efforts will need to include provision of assistance to longer-term EHR users.
【ディスカッション】
<PURPOSE>
Recent efforts to encourage meaningful use of electronic health records (EHRs) assume that widespread adoption will improve the quality of ambulatory care, especially for complex clinical conditions such as diabetes. Cross-sectional studies of typical uses of commercially available ambulatory EHRs provide conflicting evidence for an association between EHR use and improved care, and effects of longer-term EHR use in community-based primary care settings on the quality of care are not well understood.
<METHODS>
We analyzed data from 16 EHR-using and 26 non-EHR-using practices in 2 northeastern states participating in a group-randomized quality improvement trial. Measures of care were assessed for 798 patients with diabetes. We used hierarchical linear models to examine the relationship between EHR use and adherence to evidence-based diabetes care guidelines, and hierarchical logistic models to compare rates of improvement over 3 years.
<RESULTS>
EHR use was not associated with better adherence to care guidelines or a more rapid improvement in adherence. In fact, patients in practices that did not use an EHR were more likely than those in practices that used an EHR to meet all of 3 intermediate outcomes targets for hemoglobin A1c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and blood pressure at the 2-year follow-up (odds ratio = 1.67; 95% CI, 1.12-2.51). Although the quality of care improved across all practices, rates of improvement did not differ between the 2 groups.
<CONCLUSIONS>
Consistent use of an EHR over 3 years does not ensure successful use for improving the quality of diabetes care. Ongoing efforts to encourage adoption and meaningful use of EHRs in primary care should focus on ensuring that use succeeds in improving care. These efforts will need to include provision of assistance to longer-term EHR users.
【開催日】
2012年6月20日