【文献名】 Erika Ringdahl, Sandesh Pndit. Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83(11):1287-1292. 【要約】 <Background> Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease occurring primarily in older adults. It is characterized by erosion of the articular cartilage, hypertrophy of bone at the margins (i.e., osteophytes), and subchondral sclerosis.1 Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States,2 and osteoarthritis is the most common condition affecting synovial joints.3 Despite its widespread prevalence, however, the precise etiology, pathogenesis, and progression of osteoarthritis are unknown. Several factors may make a person vulnerable to the disease (Table 1).
<Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis> The differential diagnosis of chronic knee pain is given in original paper (table2). The criteria for diagnosing knee osteoarthritis are based on the presence of knee pain plus at least three of the six clinical characteristics listed in Table 3.5,6 The addition of laboratory and radiographic criteria enchances the diag- nostic accuracy; however, these tests are not necessary for all patients. In most patients, the history, physical examination, and radiography are all that is needed.
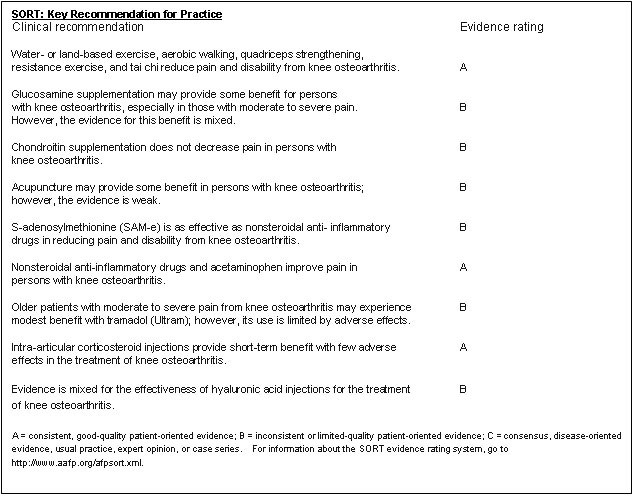
The evidence ratings of treatment of knee osteoarthritis are below. # The use of braces and heel wedges may also be effective. There is some evidence that the use of a lateral heel wedge decreases the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Similar evidence suggests that a brace and lateral wedge insole may have a small beneficial effect. # Ginger may provide some clinical benefit in patients with knee osteoarthritis; patients who took 255mg of ginger extract twice daily had a reduction in pain (63% compared with 50% in the placebo group). # Topical NSAIDs were superior to placebo in relieving pain, but only for the first two weeks of treatment. Topical NSAIDs were less effective than oral NSAIDs. # Arthroscopic surgery is not an appropriate treatment unless there is evidence of loose bodies or mechanical symptoms such as locking, giving way, or catching. # The main indication for total knee arhtroplasty is relief of pain associated with knee osteoarthritis if nonsurgical treatment has been ineffective. The complication rate of total knee replacement is 5.4% of patients.
【開催日】
2011年6月15日